What’s New in v1.2.0
Yichao Hua
2025-05-16
News.RmdNew Features and Enhancements in v1.2.0
Dark Theme Support for Feature Plot Visualization
The FeaturePlot3 and FeaturePlot3.grid
functions now support a dark theme option, providing better contrast for
visualizing gene expression patterns, particularly in presentations or
low-light environments:
library(Seurat)
library(SeuratExtend)
# Using dark theme with FeaturePlot3
FeaturePlot3(
pbmc,
color = "rgb",
feature.1 = "CD3D",
feature.2 = "CD14",
feature.3 = "CD79A",
pt.size = 1,
dark.theme = TRUE
)
New Violin Plot Styling Options
The VlnPlot2 function now supports an “outline” style
option, which uses white-filled violins with colored outlines instead of
the default filled style:
# Outline style for violin plots
genes <- c("CD3D", "CD14", "CD79A")
VlnPlot2(pbmc, features = genes, style = "outline", ncol = 1)
New ClusterDistrPlot Function
The new ClusterDistrPlot function extends
ClusterDistrBar to allow comparison of cluster distribution
patterns between experimental conditions. When the
condition parameter is provided, it creates boxplots
grouped by condition instead of stacked bars:
# Compare cluster distribution between conditions
ClusterDistrPlot(
origin = pbmc$sample_id,
cluster = pbmc$cluster,
condition = pbmc$condition
)
This function inherits styling options from VlnPlot2
when in boxplot mode, making it highly versatile for comparing cell type
proportions across experimental groups.
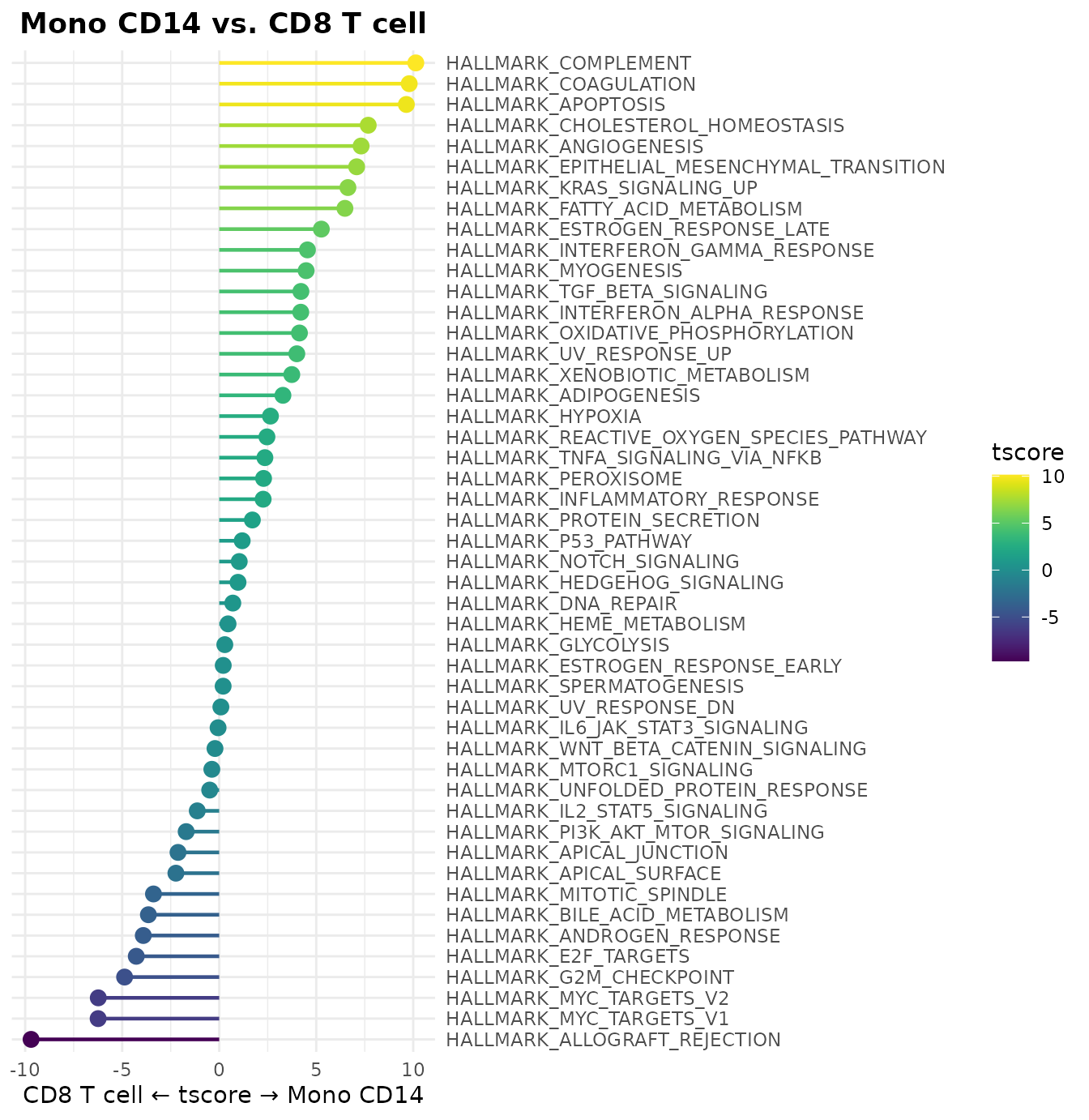
Enhanced Log Fold Change Options in Differential Analysis Plots
Both WaterfallPlot and VolcanoPlot
functions now support different logarithm bases for fold change
calculations through the log.base parameter:
# Using log base 2 for fold change calculations in WaterfallPlot
WaterfallPlot(
pbmc,
group.by = "cluster",
features = VariableFeatures(pbmc)[1:80],
ident.1 = "Mono CD14",
ident.2 = "CD8 T cell",
length = "logFC",
log.base = "2", # Use log2 instead of natural log
top.n = 20)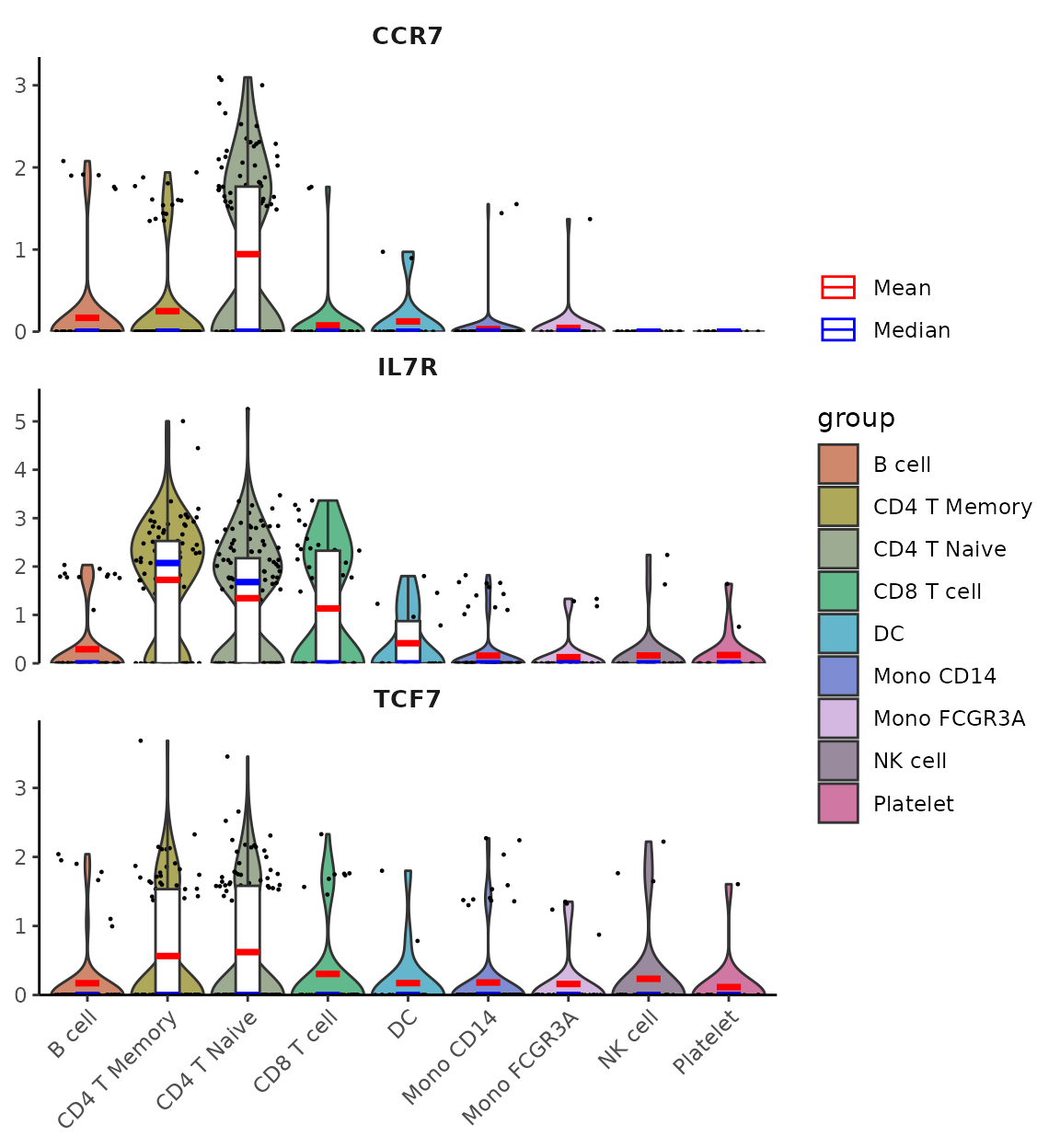
# Using log base 2 in VolcanoPlot
VolcanoPlot(
pbmc,
ident.1 = "B cell",
ident.2 = "CD8 T cell",
log.base = "2" # Use log2 instead of natural log
)
Available options include: - log.base = "e": Natural
logarithm (default) - log.base = "2": Log base 2 -
log.base = "10": Log base 10 - Any numeric value for custom
bases
Color Scheme Updates
New “Bright” Color Scheme and Default Change
A new vibrant color scheme “bright” has been added for visualizations requiring higher contrast:
library(cowplot)
DimPlot2(pbmc, features = c("orig.ident", "cluster"), cols = "bright", ncol = 2, theme = NoAxes())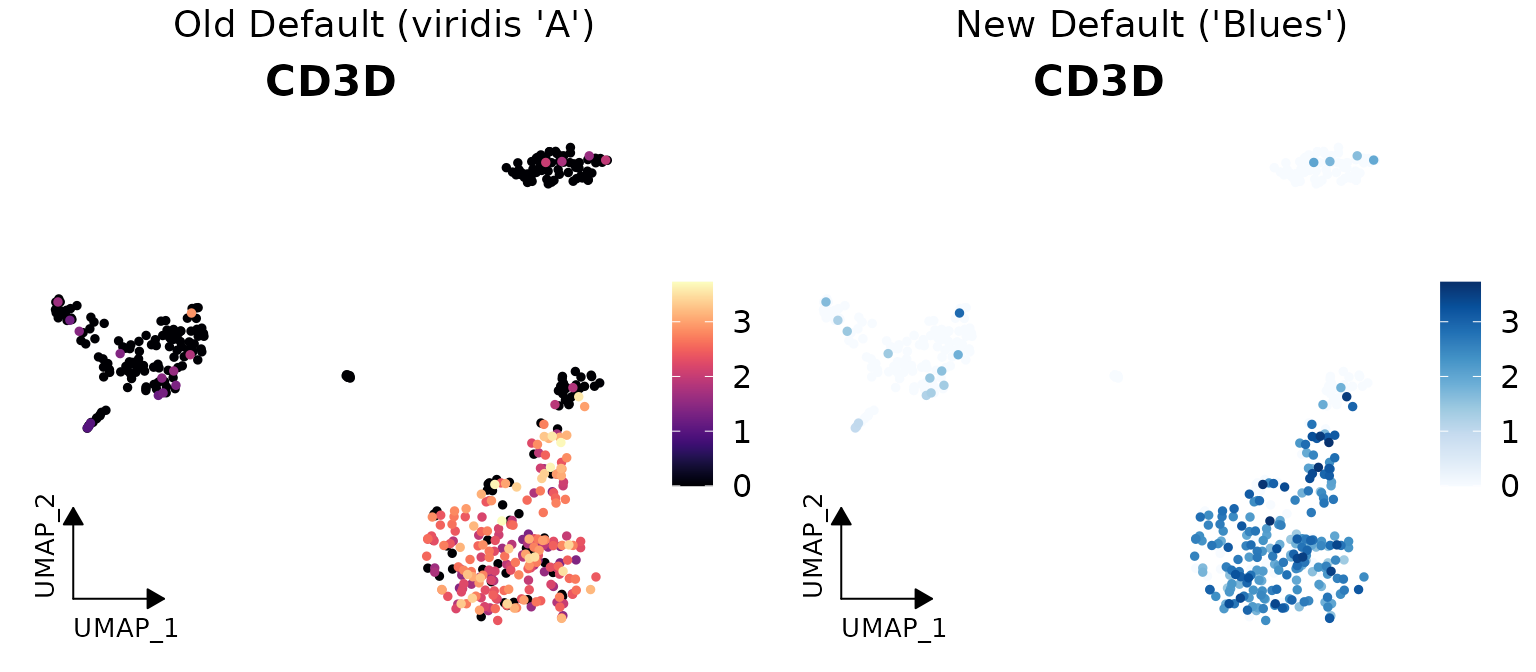
Based on user feedback, the default discrete color scheme has been
changed from “default” (darker theme) to “light” to avoid color
inconsistency in DimPlot2 when toggling between labeled and
unlabeled displays.
If you prefer to retain the original “default” (darker) color scheme, you can use:
seu <- save_colors(seu, col_list = list("discrete" = "default"))Enhanced Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) Capabilities
Improved Database Management
SeuratExtend now offers enhanced ways to manage and update the GO and Reactome databases used in your GSEA analyses:
# Install specific versions of SeuratExtendData for different database releases
install_SeuratExtendData("latest") # Latest version (April 2025 data)
install_SeuratExtendData("stable") # Stable version (January 2020 data)
install_SeuratExtendData("v0.2.1") # Specific version with January 2020 datasets
install_SeuratExtendData("v0.3.0") # Specific version with April 2025 datasetsThis ensures compatibility with specific analysis workflows or when you need to match results from previous studies.
Creating and Using Custom Databases
SeuratExtend now provides a more streamlined workflow for creating and using custom GO or Reactome databases:
# Load custom database
custom_GO_Data <- readRDS("path/to/your/GO_Data.rds")
# Use with SeuratExtend by assigning to global environment
GO_Data <- custom_GO_Data
# Run analysis
seu <- GeneSetAnalysisGO(seu, parent = "immune_system_process")
# When done, remove the global variable
rm(GO_Data)This feature is particularly useful for: - Using the latest database updates - Creating databases for additional model organisms - Developing custom pathway collections
For detailed documentation on creating custom databases, SeuratExtend provides comprehensive guides accessible through:
Apple Silicon (M1/M2/M3/M4) Support for Trajectory Analysis
SeuratExtend v1.2.0 adds support for Apple Silicon chips (M1/M2/M3/M4), allowing macOS users to run Python-based trajectory analysis tools. However, this support comes with specific limitations that require following a particular workflow to avoid R session crashes:
# IMPORTANT: Apple Silicon users MUST initialize Python environment BEFORE loading any data
library(SeuratExtend)
activate_python() # Must call this function FIRST to prevent memory-related crashes
# Only THEN load your data and proceed with analysis
seu <- readRDS("path/to/seurat_object.rds")Important Considerations:
- On Apple Silicon, memory management issues exist between R and Python, especially when performing operations like PCA on AnnData objects
- If R objects are loaded before calling Python functions, the R session will likely crash
- You must start a fresh R session and call
activate_python()before loading any data - This initialization sequence is necessary when using tools like scVelo, Palantir, or CellRank
Despite these limitations, the
create_condaenv_seuratextend() function now automatically
detects Apple Silicon and uses the appropriate configuration, enabling
Mac users to run:
- scVelo: for RNA velocity analysis
- Palantir: for cell fate determination and pseudotime analysis
- CellRank: for trajectory analysis
- MAGIC: for gene expression denoising and smoothing
Bug Fixes and Improvements
Several important bug fixes and enhancements have been implemented based on user feedback:
- scVelo Functions: Fixed issues related to scVelo functionality, addressing reported bugs in GitHub issue #30.
-
DotPlot2: Fixed bugs affecting the appearance and
functionality of the
DotPlot2function (GitHub issues #22 and #29). - Palantir Windows Compatibility: Fixed compatibility issues for Palantir functions on Windows systems (GitHub issue #24).
-
Color Palette Enhancement: Increased the color
limit from 50 to 80 colors in the
color_profunction, allowing for more color options in visualizations. -
ClusterDistrBar Validation: Added input validation
to the
ClusterDistrBarfunction to prevent errors from invalid inputs. - RColorBrewer Sequential Palettes: Enhanced the lightest colors in sequential color palettes to improve visibility against white backgrounds.
-
VlnPlot2 Documentation: Added detailed explanations
of the statistics options in the
VlnPlot2function documentation. -
Package Installation: Fixed issues in the internal
importfunction related to automatic package installation. -
WaterfallPlot Improvements:
- Added automatic adjustment of x-axis text angle and alignment for better readability
- Added option to display borders around bars for improved visual clarity
New Features and Enhancements in v1.1.0
New Visualization Functions
Enhanced Dot Plots with DotPlot2
A new function DotPlot2 has been introduced, combining
dot size (percent of expressing cells) with color intensity (average
expression) for more informative visualizations:
library(Seurat)
library(SeuratExtend)
# With grouped features
grouped_features <- list(
"B_cell_markers" = c("MS4A1", "CD79A"),
"T_cell_markers" = c("CD3D", "CD8A", "IL7R"),
"Myeloid_markers" = c("CD14", "FCGR3A", "S100A8")
)
DotPlot2(pbmc, features = grouped_features)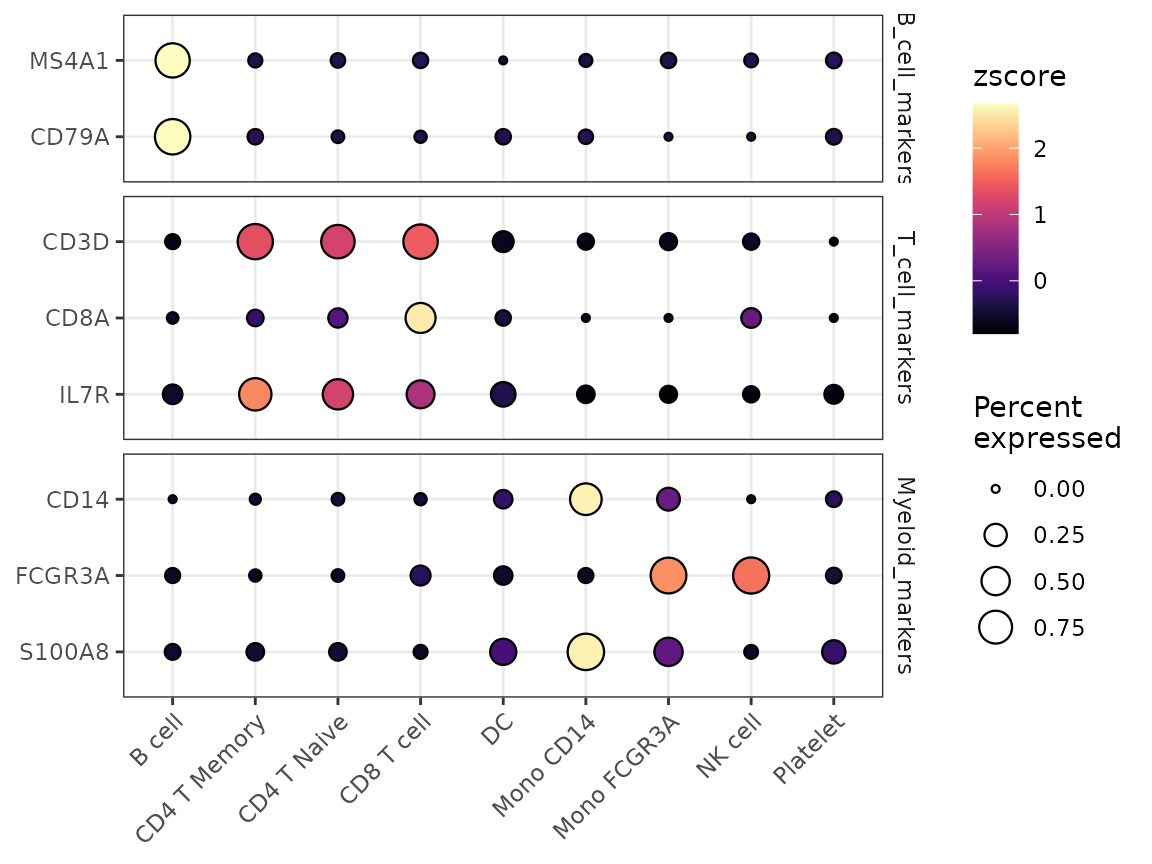
New Volcano Plots
The new VolcanoPlot function provides statistical
visualization of differential expression:
VolcanoPlot(pbmc,
ident.1 = "B cell",
ident.2 = "CD8 T cell")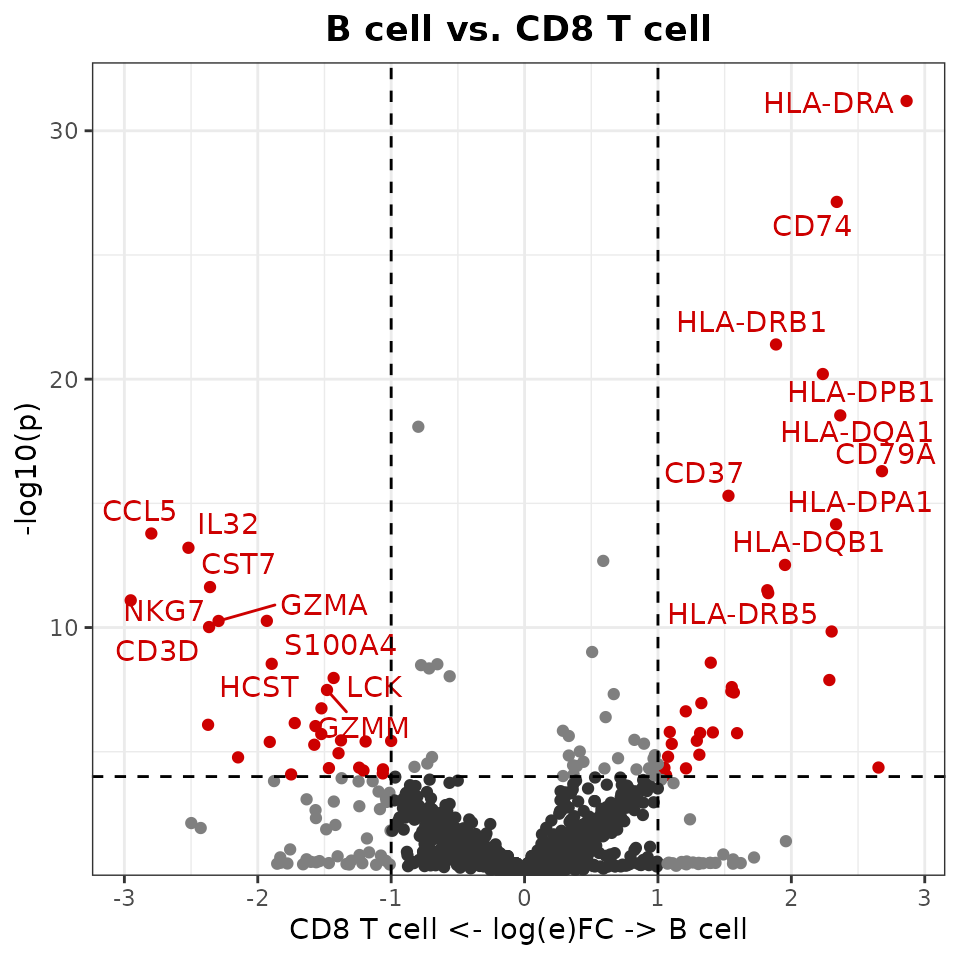
UMAP Arrow Annotations
Added theme_umap_arrows for simplified axis indicators
on dimension reduction plots:
DimPlot2(pbmc, theme = NoAxes()) + theme_umap_arrows()
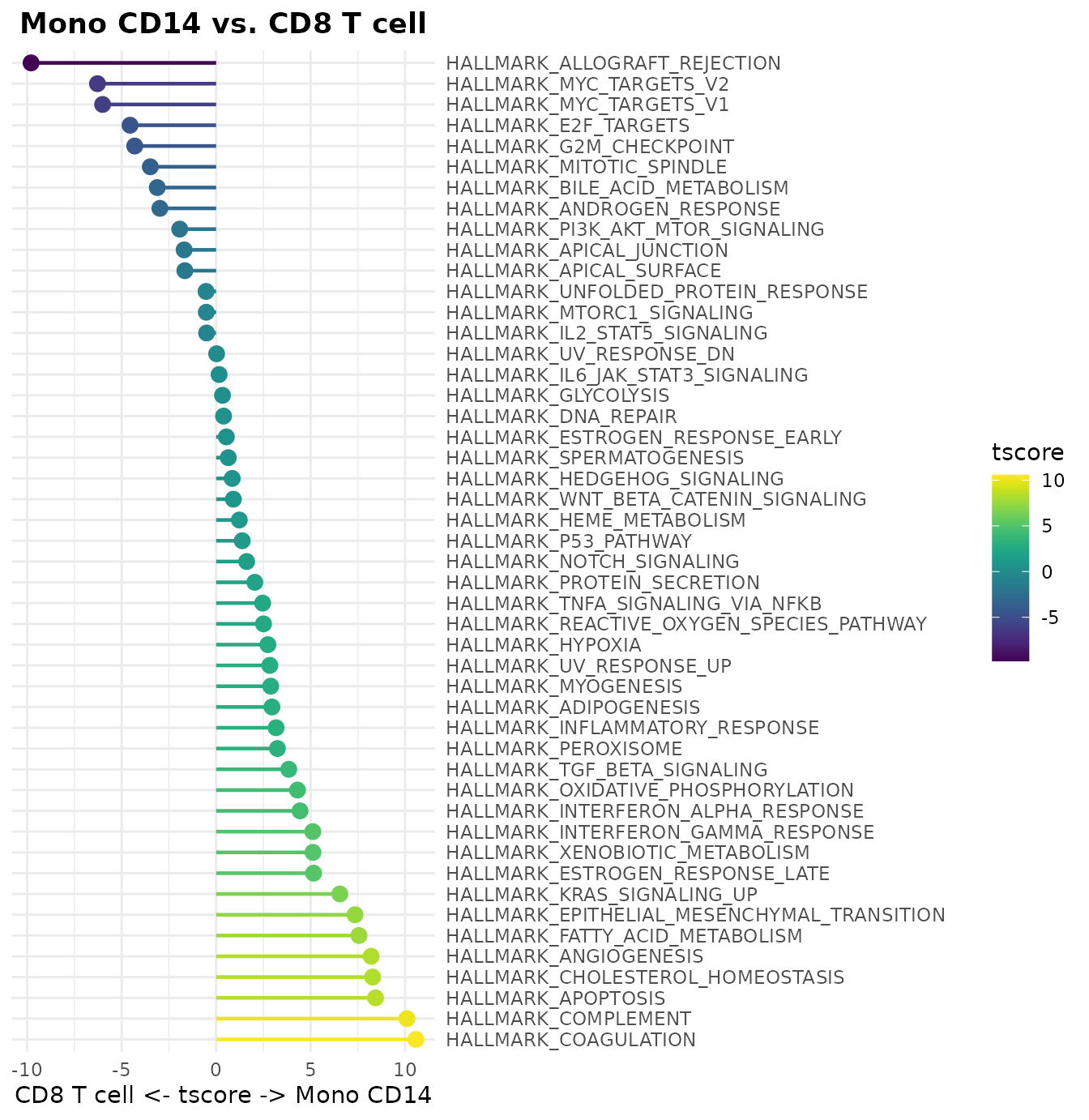
New WaterfallPlot Style: “segment”
Added a new visualization style “segment” to WaterfallPlot, providing an alternative way to display differences between conditions:
# Prepare data
pbmc <- GeneSetAnalysis(pbmc, genesets = hall50$human)
matr <- pbmc@misc$AUCell$genesets
# Create a plot using the new segment style
WaterfallPlot(
matr,
f = pbmc$cluster,
ident.1 = "Mono CD14",
ident.2 = "CD8 T cell",
style = "segment",
color_theme = "D"
)
Color Scheme Updates
New Default Color Schemes
Two major color scheme changes have been implemented in v1.1.0:
- For continuous variables: Changed from viridis “A” to RColorBrewer “Blues”
- For heatmaps: Updated from
c(low = muted("blue"), mid = "white", high = muted("red"))to “BuRd”
Here are visual comparisons of the old and new defaults:
Continuous Variable Color Scheme
# Create a side-by-side comparison for continuous variables
library(cowplot)
library(ggpubr)
# Old default (viridis "A")
p1 <- DimPlot2(pbmc,
features = "CD3D",
cols = "A", # Old default
theme = theme_umap_arrows())
# New default (Blues)
p2 <- DimPlot2(pbmc,
features = "CD3D",
theme = theme_umap_arrows())
plot_grid(
annotate_figure(p1, top = text_grob("Old Default (viridis 'A')", size = 14)),
annotate_figure(p2, top = text_grob("New Default ('Blues')", size = 14)),
ncol = 2)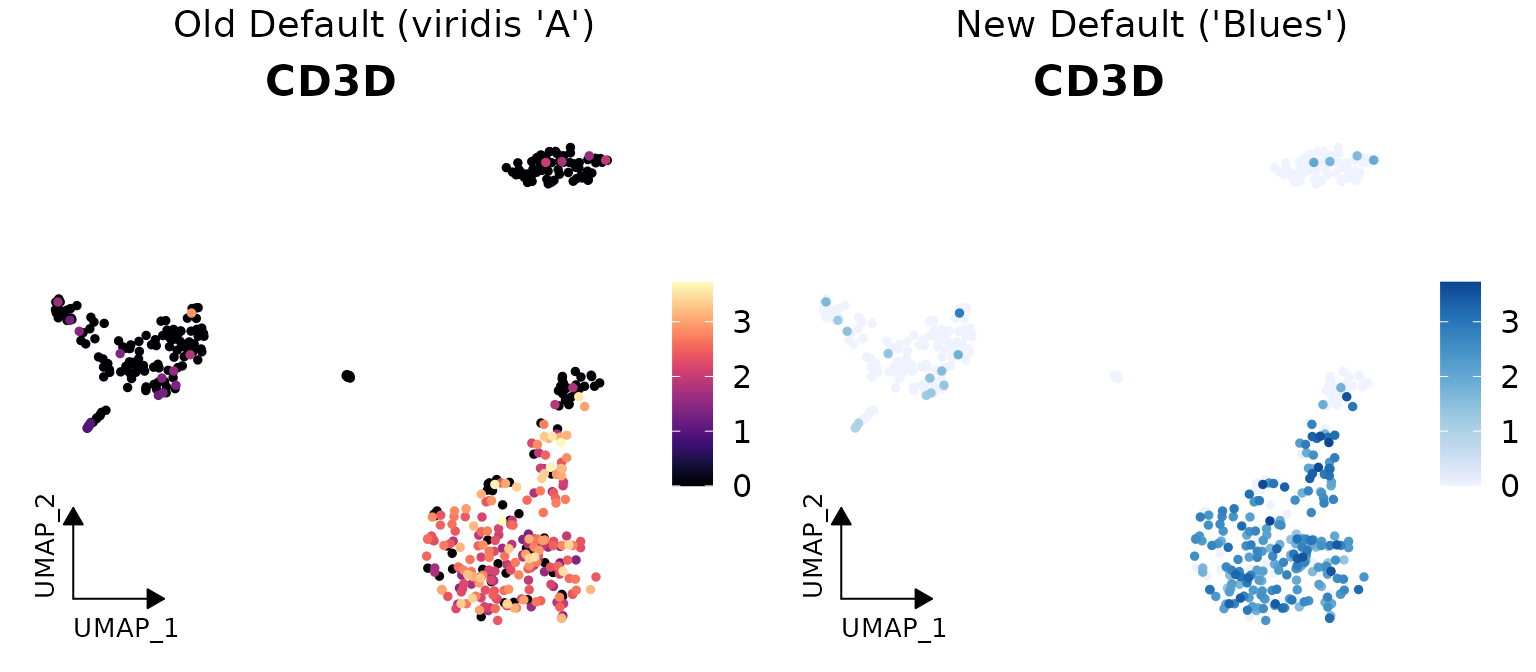
Heatmap Color Scheme
# Calculate data for heatmap
genes <- VariableFeatures(pbmc)
toplot <- CalcStats(pbmc, features = genes, method = "zscore", order = "p", n = 4)
# Create side-by-side heatmap comparison
p1 <- Heatmap(toplot,
color_scheme = c(low = scales::muted("blue"),
mid = "white",
high = scales::muted("red")), # Old default
lab_fill = "zscore") +
ggtitle("Old Default (blue-white-red)")
p2 <- Heatmap(toplot,
lab_fill = "zscore") + # New default (BuRd) is automatically applied
ggtitle("New Default ('BuRd')")
plot_grid(p1, p2, ncol = 2)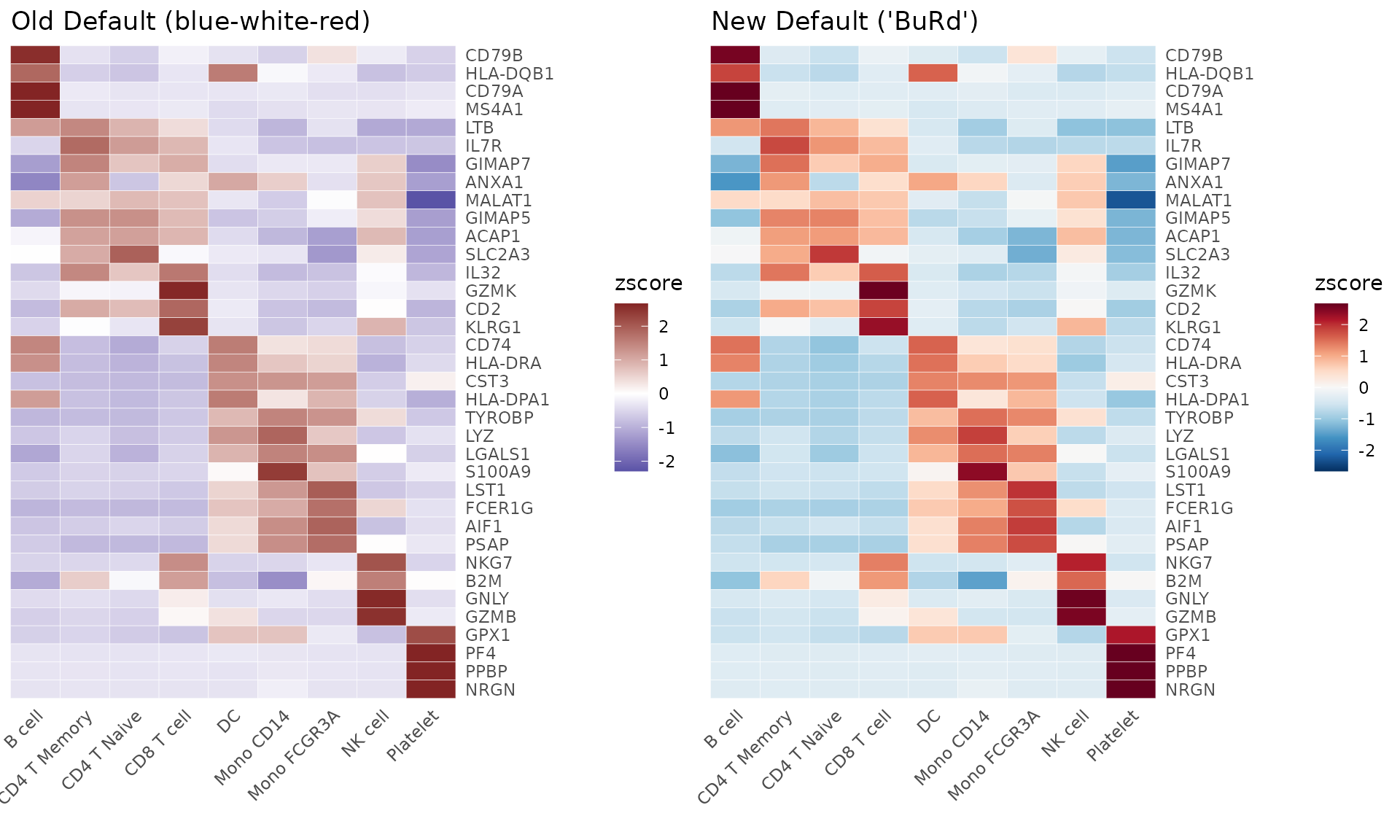
To revert to previous color schemes: - For continuous variables: Use
cols = "A" - For heatmaps: Use
color_scheme = c(low = scales::muted("blue"), mid = "white", high = scales::muted("red"))
Feature Enhancements
-
VlnPlot2: Now supports both
stats.methodandstat.methodas parameter inputs (#10) -
ClusterDistrBar: Added
reverse_orderparameter to adjust the stacking order (#11) - WaterfallPlot: Set upper limit for -log10(p) values to avoid NA issues (#14)
- DimPlot2: Improved automatic point size adjustment and fixed point display issues in raster mode (#17)
- show_col2: Function is now exported, allowing users to knit Visualization.Rmd without issues (#8)
Bug Fixes
-
VlnPlot2: Now explicitly uses
dplyr::selectinternally to avoid conflicts with other packages’ select functions (#5, #10) - ClusterDistrBar: Fixed display issues when factor levels are numeric (e.g., seurat_clusters)
Documentation Updates
Conda Environment Setup
The create_condaenv_seuratextend() function
documentation has been updated with important compatibility
information:
- Currently supported and tested on:
- Windows
- Intel-based macOS (not Apple Silicon/M1/M2)
- Linux (Ubuntu 20.04)
Note for Apple Silicon Users: The function is not currently compatible with Apple Silicon/M1/M2 devices (#7). Users with Apple Silicon devices who are interested in contributing to the development of M1/M2 support are welcome to reach out via GitHub Issues.
Windows-Specific File Download
When downloading loom files (which are HDF5-based binary files) on
Windows, it’s essential to use mode = "wb" in the
download.file() function:
# Example for Windows users
download.file("https://example.com/file.loom", "file.loom", mode = "wb")This prevents Windows from modifying line endings in the binary file, which would corrupt the HDF5 format. Mac and Linux users don’t require this parameter, but including it is harmless.
## R version 4.4.0 (2024-04-24)
## Platform: x86_64-pc-linux-gnu
## Running under: Ubuntu 20.04.6 LTS
##
## Matrix products: default
## BLAS: /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/blas/libblas.so.3.9.0
## LAPACK: /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/lapack/liblapack.so.3.9.0
##
## locale:
## [1] LC_CTYPE=en_US.UTF-8 LC_NUMERIC=C
## [3] LC_TIME=de_BE.UTF-8 LC_COLLATE=en_US.UTF-8
## [5] LC_MONETARY=de_BE.UTF-8 LC_MESSAGES=en_US.UTF-8
## [7] LC_PAPER=de_BE.UTF-8 LC_NAME=C
## [9] LC_ADDRESS=C LC_TELEPHONE=C
## [11] LC_MEASUREMENT=de_BE.UTF-8 LC_IDENTIFICATION=C
##
## time zone: Europe/Brussels
## tzcode source: system (glibc)
##
## attached base packages:
## [1] stats4 grid stats graphics grDevices utils datasets
## [8] methods base
##
## other attached packages:
## [1] rlang_1.1.4 DelayedMatrixStats_1.26.0
## [3] DelayedArray_0.30.1 SparseArray_1.4.8
## [5] S4Arrays_1.4.1 abind_1.4-5
## [7] IRanges_2.38.1 S4Vectors_0.42.1
## [9] MatrixGenerics_1.16.0 matrixStats_1.3.0
## [11] BiocGenerics_0.50.0 mosaic_1.9.1
## [13] mosaicData_0.20.4 ggformula_0.12.0
## [15] Matrix_1.7-0 lattice_0.22-6
## [17] cowplot_1.1.3 ggrepel_0.9.5
## [19] viridis_0.6.5 viridisLite_0.4.2
## [21] scales_1.3.0 tidyr_1.3.1
## [23] ggbeeswarm_0.7.2 rlist_0.4.6.2
## [25] RColorBrewer_1.1-3 dplyr_1.1.4
## [27] ggpubr_0.6.0 ggplot2_3.5.1
## [29] reshape2_1.4.4 SeuratExtend_1.2.0
## [31] SeuratExtendData_0.3.0 Seurat_5.2.1
## [33] SeuratObject_5.0.2 sp_2.1-4
##
## loaded via a namespace (and not attached):
## [1] RcppAnnoy_0.0.22 splines_4.4.0 later_1.3.2
## [4] tibble_3.2.1 polyclip_1.10-6 fastDummies_1.7.3
## [7] lifecycle_1.0.4 rstatix_0.7.2 globals_0.16.3
## [10] MASS_7.3-61 backports_1.5.0 magrittr_2.0.3
## [13] plotly_4.10.4 sass_0.4.9 rmarkdown_2.29
## [16] jquerylib_0.1.4 yaml_2.3.9 httpuv_1.6.15
## [19] sctransform_0.4.1 spam_2.10-0 spatstat.sparse_3.1-0
## [22] reticulate_1.38.0 pbapply_1.7-2 zlibbioc_1.50.0
## [25] Rtsne_0.17 purrr_1.0.2 labelled_2.13.0
## [28] irlba_2.3.5.1 listenv_0.9.1 spatstat.utils_3.0-5
## [31] goftest_1.2-3 RSpectra_0.16-1 spatstat.random_3.2-3
## [34] fitdistrplus_1.2-1 parallelly_1.37.1 pkgdown_2.0.7
## [37] codetools_0.2-20 tidyselect_1.2.1 farver_2.1.2
## [40] spatstat.explore_3.2-7 jsonlite_1.8.8 progressr_0.14.0
## [43] ggridges_0.5.6 survival_3.7-0 systemfonts_1.1.0
## [46] tools_4.4.0 ragg_1.3.2 ica_1.0-3
## [49] Rcpp_1.0.13 glue_1.7.0 gridExtra_2.3
## [52] xfun_0.45 withr_3.0.0 fastmap_1.2.0
## [55] fansi_1.0.6 digest_0.6.36 R6_2.5.1
## [58] mime_0.12 textshaping_0.4.0 colorspace_2.1-0
## [61] scattermore_1.2 tensor_1.5 spatstat.data_3.1-2
## [64] utf8_1.2.4 generics_0.1.3 data.table_1.15.4
## [67] httr_1.4.7 htmlwidgets_1.6.4 uwot_0.2.2
## [70] pkgconfig_2.0.3 gtable_0.3.5 lmtest_0.9-40
## [73] XVector_0.44.0 htmltools_0.5.8.1 carData_3.0-5
## [76] dotCall64_1.1-1 png_0.1-8 knitr_1.48
## [79] rstudioapi_0.16.0 nlme_3.1-165 cachem_1.1.0
## [82] zoo_1.8-12 stringr_1.5.1 KernSmooth_2.23-24
## [85] parallel_4.4.0 miniUI_0.1.1.1 vipor_0.4.7
## [88] desc_1.4.3 pillar_1.9.0 vctrs_0.6.5
## [91] RANN_2.6.1 promises_1.3.0 car_3.1-2
## [94] xtable_1.8-4 cluster_2.1.6 beeswarm_0.4.0
## [97] evaluate_0.24.0 cli_3.6.3 compiler_4.4.0
## [100] crayon_1.5.3 future.apply_1.11.2 ggsignif_0.6.4
## [103] labeling_0.4.3 plyr_1.8.9 forcats_1.0.0
## [106] fs_1.6.4 stringi_1.8.4 deldir_2.0-4
## [109] munsell_0.5.1 lazyeval_0.2.2 spatstat.geom_3.2-9
## [112] mosaicCore_0.9.4.0 RcppHNSW_0.6.0 hms_1.1.3
## [115] patchwork_1.2.0 sparseMatrixStats_1.16.0 future_1.33.2
## [118] shiny_1.8.1.1 highr_0.11 haven_2.5.4
## [121] ROCR_1.0-11 igraph_2.0.3 broom_1.0.6
## [124] memoise_2.0.1 bslib_0.4.2